Continuous Charge Distribution
Continuous Charge Distribution: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Continuous Charge Distribution,Line Charge Distribution,Surface Charge Distribution, etc.
Important Questions on Continuous Charge Distribution
A spherical conducting shell of inner radius and outer radius has a charge . A charge is placed at the centre of the shell.
What is the surface charge density on the (i) inner surface, (ii) outer surface of the shell?
A sphere has surface charge density . It is surrounded by a spherical shell. The surface charge density on the spherical shell is
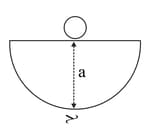
Charge is uniformly distributed over a thin half ring of radius. The electric field at the centre of the ring is
A uniformly charged conducting sphere of in diameter has a surface charge density of . Calculate the
(i) Charge on the sphere. (ii) Total electric flux coming out a Gaussian surface just enclosing the outer surface of the sphere.
Total energy per unit length of a line charge in space, from perpendicular distance to , from line charge, is given by ( denotes charge per unit length)
A charged spherical conductor has a surface charge density of . When its charge is increased by , the charge density changes by . The radius of the sphere is
Electric field at centre of semicircle of radius a having linear charge density given as
The volume charge density of a sphere of radius is represented by . So, the total charge on the sphere would be _____
The charge density of a spherical distribution is given by
What is the total charge on the distribution?
A region is space contains a total positive charge that is distributed spherically such that the volume charge density
Where is a positive constant. The value of in terms of and is
An electron moves in the field produced by a charged sphere of radius along the radius connecting the points separated by and from the centre of the sphere. The velocity of the electron changes thereby from to If the surface charge (in ) density of the sphere is then find . (Mass of electron
Two isolated hollow spheres of radius and are charged to volts and volts respectively. Now the smaller sphere is inserted into the bigger sphere such that net charge on each sphere reamin same, then the potential difference between the two spheres becomes . Find .
Two conducting spheres of radii and have equal surface charge densities. The ratio of their charges is ___.
Describe linear charge density. Write its SI unit.
What is volume charge density? Write its SI unit.
Describe linear charge density.
What is volume charge distribution?
Two conducting spheres of radii and have equal surface charge densities. The ratio of their charges is ___.
Explain the term volume charge density. Write its SI unit.
Explain the term surface charge density. Write its Sl unit.
